NDC Clinical Guidelines Induction of Lactation Part 1. The most reliable element in non-puerperal induction of lactation protocols is stimulation of the breasts and nipples + frequent flexible milk removal
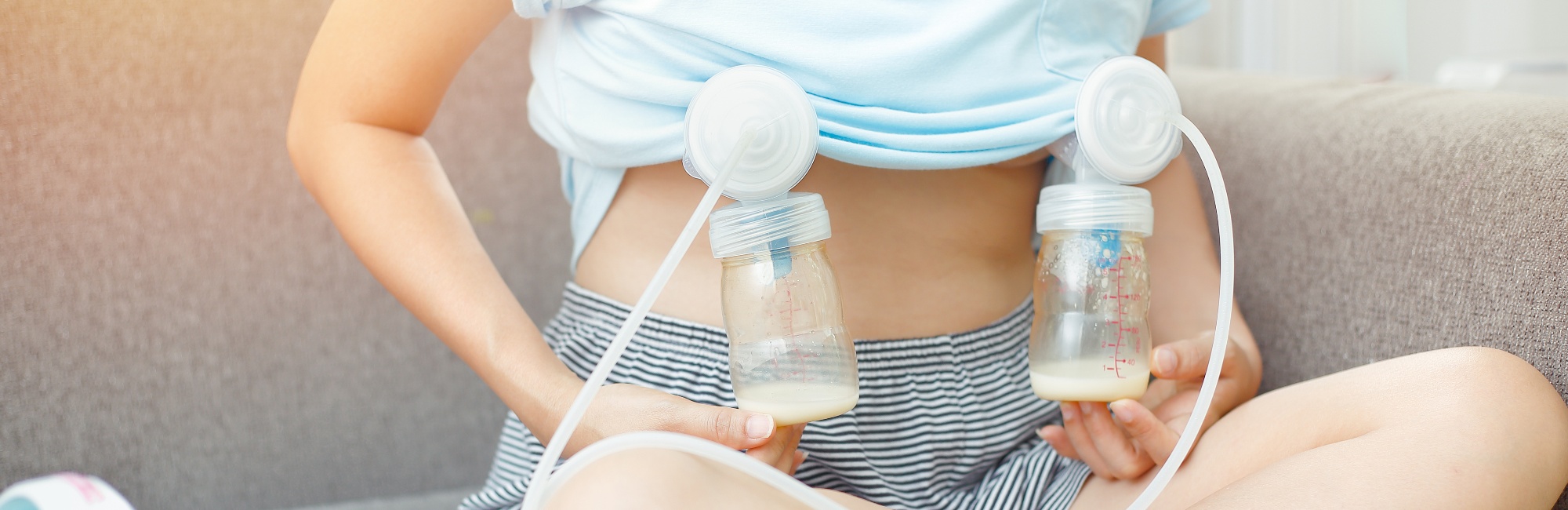
How should a patient prepare for pumping to induce lactation?
Your patient will find nipple and breast stimulation most efficient if they use a hospital grade double-flanged electric pump.
Some patients like to use a wearable pump too, for convenience. There are risks associated with a wearable pump though such as
-
Moisture associated skin damage
-
Poorer fit with increased risk of nipple pain or damage
-
Breast inflammation.
This is why I recommend a hand held hospital grade double pump as the most important item, and only careful intermittent use of the wearable pump.
The NDC guidelines part 3: manual stimulation and pumping for induction of lactation
-
Your patient might choose to start some manual stimulation of their breasts prior to commencing pumping, for example, during hormonal preparation. This could involve stroking or rolling the nipple, or massaging the breast.
-
Educate your patient about hand expression of breastmilk so that the patient knows how to do this if they want to down the track. You can find the free resource for patients on how to hand express here.
- There's no evidence to suggest that manual stimulation of the nipple and breasts improves outcomes, and prescribing this as a necessary part of induction may add unnecessary burden.
-
Low to medium setting on pump (ensure comfort)
-
Ensure properly fitted flange, experiment between sizes for comfort
-
Pump day and night for at least four weeks
-
A gradual ramp up in frequency over the first week may feel more manageable, just a few times a day at first and for just a short period of time. There is no need to be prescriptive about this, as the patient can ramp up according to need and nipple comfort.
-
Pump every two or three hours for ten minutes or so (ten minutes of stimulation each breast). Focus on frequency rather than duration, and pumping sessions don't need to occur regularly but should add up to seven or more pumps during waking hours.
-
Pump once during the night. This does not need to be between 1 am and 5 am, because the belief that the elevated prolactin levels typically found during this time will benefit milk production misunderstands the science. You can find out about prolactin levels here.
Frequent and flexible breastfeeds, and the usual strategies taken by NDC or the Possums programs to support breastfeeding and lactation, are applied once the baby arrives.
Recommended resources
Research about induction of lactation in transgender patients
Induction of lactation: taking a history and why each question matters
Case report of preparation for induction of lactation in a cisgender woman (NDC Clinical Guidelines)
NDC Co-lactation Feeding Plan (to be adapted adapted)
Selected references
McBride GM, Stevenson R, Zizzo G, Rumbold AR, Amir LH, Keir AK, et al. Use and experience of galactogogues while breastfeeding among Australian women. Plos One. 2021;16(7):e0254049
Other references available here.
-fotor-20240115155339.jpg)